What is E-Invoicing?
E-Invoicing is a process that generates invoices and related documentation in electronic file format using an Electronic Billing System (EBS), allowing billing information to be transferred in real time between the buyer, seller, and tax authority.
Global Evolution
E-invoicing has gained global recognition, owing to the requirement for enhanced efficiency and regulatory compliance.
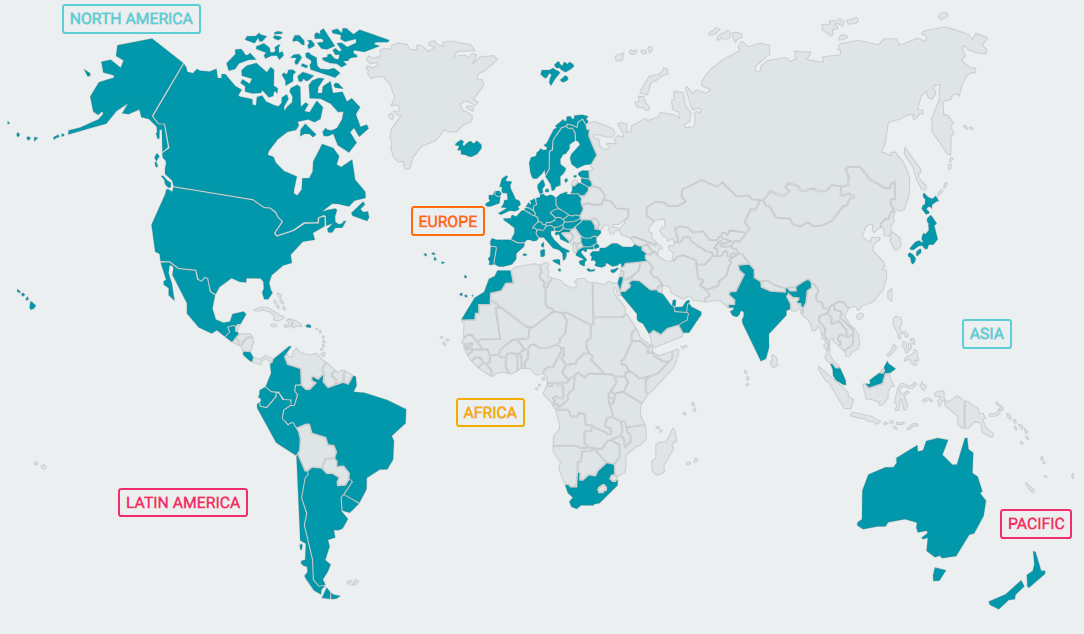
Europe | APAC | Americas | Africa |
Italy | India | Chile | Kenya |
France | China | Canada | Ethiopia |
Spain | Saudi Arabia | Brazil | Tanzania |
Portugal | Singapore | Argentina | Rwanda |
Poland | Hong Kong | Venezuela | Malawi |
Greece | Taiwan | Ecuador | Mozambique |
Turkey | South Korea | Mexico | Zimbabwe |
Sweden | Japan | Peru | Uganda |
Czech Republic | Australia | Uruguay | Zambia |
E-Invoicing in Africa
Countries like Italy, Mexico, and Brazil have pushed businesses to use e-invoicing to combat tax evasion and streamline financial operations.
The European Union has also issued detectives encouraging member states to use e-invoicing, notably in public purchasing.
Legal Provisions
Mauritius' legislative foundation for e-invoicing is created by the Value Added Tax Act.
The Mauritius Revenue Authority (MRA) has been authorized to develop and manage e-invoicing, ensuring tax compliance and fostering transparency in commercial transactions.
Specific rules and laws have been created to assist in this transition.
20A. E-invoicing system
(1) Subject to such conditions as may be specified, the Director-General shall cause an Odoo e-Invoicing system to be established, allowing a business to connect electronically to the system to register all invoices, including debit notes and credit notes, generated in the course of business. Also issuing fiscal invoices to customers
(2) Every person who interacts in a business activity of the type or nature prescribed is given written notice by the Director General to issue fiscal invoices to his customers, shall acquire such equipment and software as may be required, and issue fiscal invoices to his customers on the date fixed by the Director-General.
(3) The Director-General may issue a notice under subsection (2) to any person, whether or not he is a taxable person, or makes entirely exempt supply.
(4) The Director-General shall issue such guidelines and technical specifications as he deems necessary for implementing the Odoo e-Invoicing system. Every person is required to provide fiscal invoices under subsection. Must follow the guidelines and technical specifications issues under the (1) subsection.
How the System Operates
The MRA manages the centralized platform via which Mauritius' e-invoicing system runs. Businesses create invoices in their Enterprise Business Systems (EBS), which are subsequently sent to the MRA's platform in a predetermined format.
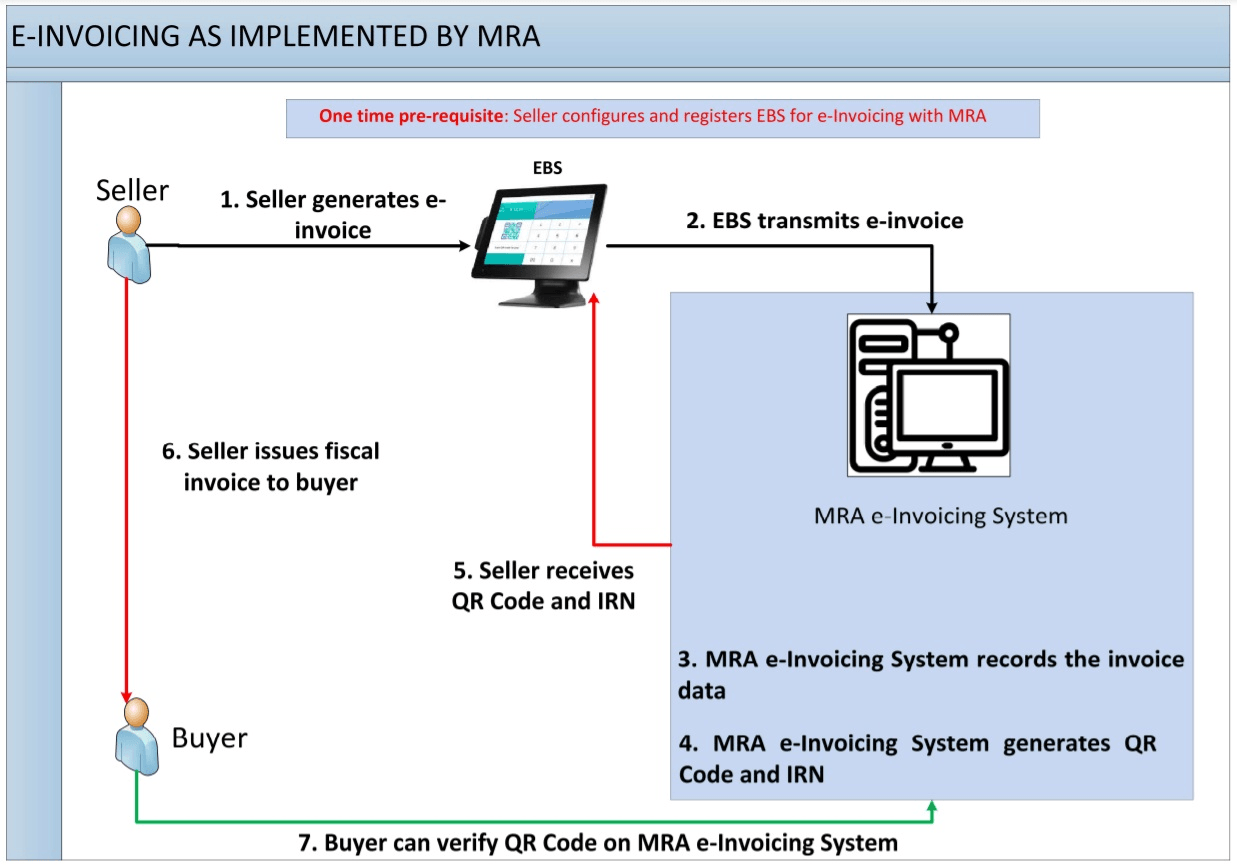
Before an invoice is forwarded to a receiver, the MRA checks it and issues it with a unique identification number. This method ensures that all transactions are captured and confirmed in real-time.
Benefits of E-Invoicing
E-invoicing provides many benefits, including:
- Increased Efficiency: Automated processing saves time and effort on invoicing.
- Cost Savings: Reduced costs for paper, printing, and delivery.
- Accuracy: Reduced errors caused by manual data entering.
- Compliance: Ensures tax compliance and reduces fraud.
- Environmental Impact: Less paper consumption promotes environmental sustainability.
Persons Concerned
Every person who:
Carries on a prescribed business activity and receives written notification from the MRA to issue fiscal invoices.
A notice may be issued to both taxable and non-taxable persons, and businesses making exempt supplies exclusively.
The e-invoicing system applies to all VAT-registered enterprises in Mauritius. This comprises major companies, small and medium-sized businesses (SMEs), and public-sector entities that engage in taxable transactions.
Furthermore, software vendors and financial institutions play an important role in providing the deployment and operation of e-invoicing.
Implication for Businesses
Businesses must modify their invoicing operations to meet Odoo e-Invoicing laws. This could include upgrading existing EBS or using new solutions compatible with the MRA platform.
Educating staff and upgrading internal procedures will smooth the transition. Non-compliance may result in penalties and hinder business operations.
A business with an e-invoicing duty is required to:
- Generate and transmit invoices in JSON format using a compliant EBS (POS, Cash Register, ERP, or Accounting Package).
- Create invoices using MRA’s basic e-invoice template.
- Use an internet connection for online transmission.
- Not to use or maintain an EBS that has not been registered with MRA or is not Odoo e-Invoicing compliant.
- The placement of any EBS may not be changed without prior notice to the MRA.
EBS – General Functions
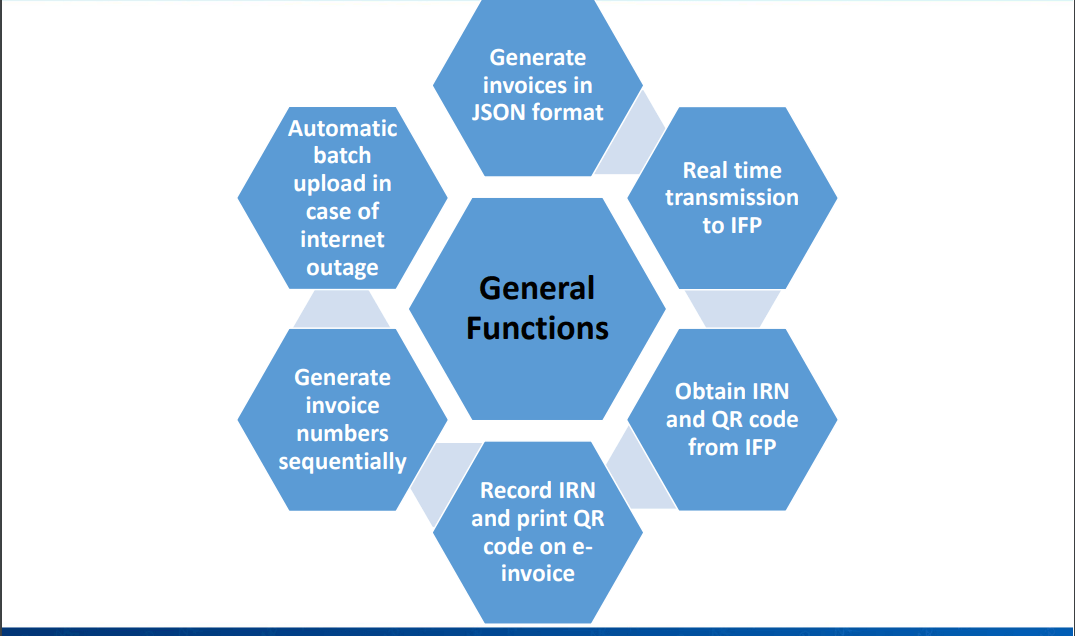
Features of a Compliant EBS
Security Features:
• Generate the previous invoice hash.
• Secure resistant EBS
• Secure resistant invoice counter
Access:
• Protected by login credentials
• Default administrator's password is disabled.
• Role-based access
Prohibited functions:
• Date and time cannot be reset
• Resetting the invoice counter is not permitted.
• No changes to fiscalized papers.
• Multiple document sequences cannot be formed.
Secure Storage:
• Save documents in a secured storage system.
Responsibility Matrix
Economic Operators
- Upgrade existing EBS to ensure e-invoicing compliance, or purchase EBS from an MRA-registered EBS solution supplier.
- Register for e-invoicing on the MRA portal.
- Register all EBS with the MRA to get unique IDs for each EBS.
- Issue fiscal invoices to customers.
EBS Solution Providers
- Register with MRA as an authorized EBS Solution Provider.
- Ensure that EBS complies with all anti-tampering features.
- Use test labs to determine the efficacy and compliance of EBS.
- Self-certify the manufacturer and model of the EBS as compliant.
- A registration with the MRA is required for both the EBS Solution Provider and his EBS before it can be sold, rented, or made available.
- Report any defects or misuse of a registered EBS.
MRA
- Provide test labs for EBS solution providers.
- Provide an e-registration gateway to register EBS once the above testing is concluded.
- Set up the invoice fiscalisation platform (IFP).
- Give EBS solution providers access to APIs so they can interact with the IFP.
- Portal/Helpdesk for complaints and reporting system outages.
- Names of compliant EBS solution providers will be published on the MRA website.
- The portal allows the general public to verify invoices.
General Public (Buyers)
- Obtain a paper or electronic fiscal receipt for each purchase.
- Check the credibility of fiscal receipts utilizing mobile apps or web.
- Report any suspicious receipt to the MRA.
The Phases Involved
The implementation of e-invoicing in Mauritius includes various steps:
- Planning: Setting up the regulatory framework and technical prerequisites.
- Development: Developing and testing the e-invoicing platform.
- Pilot Testing: Initial deployment to selected businesses for feedback and changes.
- Full Rollout: All VAT-registered enterprises must comply with the implementation.
- Continuous Improvement: Continuous upgrades and improvements based on customer feedback and technology breakthroughs.
MRA E-Invoicing Publications
The MRA has issued several papers to help businesses navigate the Odoo e-Invoicing adoption process.
EBS Functional Specifications:
Explains the features of a compliant EBS, including general functions, security features, and prohibited features.
E-Invoicing Guide for Software Developers, Including Video (NonTechnical)
Provides a general guidance on:
- How to access and browse the Developer Portal.
- Steps for Making an EBS Compliant with the MRA e-Invoicing System.
- How to test the EBS after the necessary changes have been made to ensure compliance with the MRA Odoo e-Invoicing system.
Standard E-Invoice Template
Provides the required format of an e-invoice and specifies the mandatory and optional fields.
FAQs
- A collection of the most popular questions and answers on E-Invoicing.
- These include thorough guidelines, technical requirements, frequently asked questions, and training materials, as previously discussed.
- Businesses are recommended to check these publications regularly to stay up to date on the latest developments and best practices.
Conclusion
The implementation of e-invoicing in Mauritius represents a significant step toward modernizing the country’s financial system.
Businesses that embrace digital transformation can increase productivity, lower expenses, and ensure tax compliance.
Collaboration among the MRA, businesses, and technology suppliers is important for the effective implementation of e-invoicing, opening the way for a more transparent and efficient economy.


