Streamline Your Ledgers with Odoo 17 Anglo-Saxon
Most businesses can use Odoo's accounting features, although Anglo-Saxon is an unusual approach available exclusively in the enterprise edition. Revenue is recorded during the selling process rather than the purchase.
Odoo offers two accounting methods:
- Regular (most common): Records product cost when purchased, potentially showing a loss for businesses buying in bulk.
- Anglo-Saxon (rare): Records product cost only when sold or used, ideal for high-volume purchases (like raw materials for manufacturing).
First, turn on developer mode and check the Odoo 17 accounting module configuration settings to make sure Anglo-Saxon accounting is enabled.
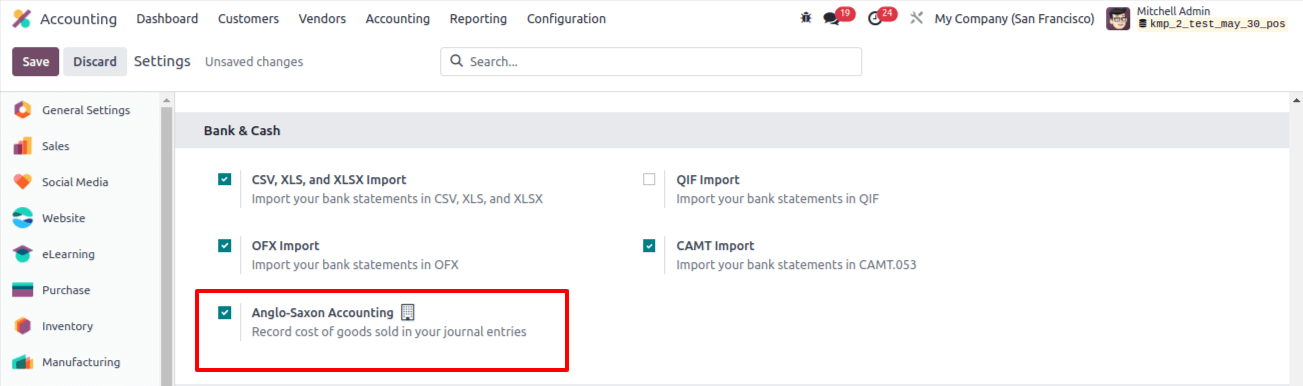
As was previously mentioned, under Anglo-Saxon accounting, costs are only recorded at the time the acquired item is sold. Despite having been purchased, the items are still considered assets. As a result, in this case, automated inventory valuation is required. To find Automated inventory valuation, navigate to the relevant product category.
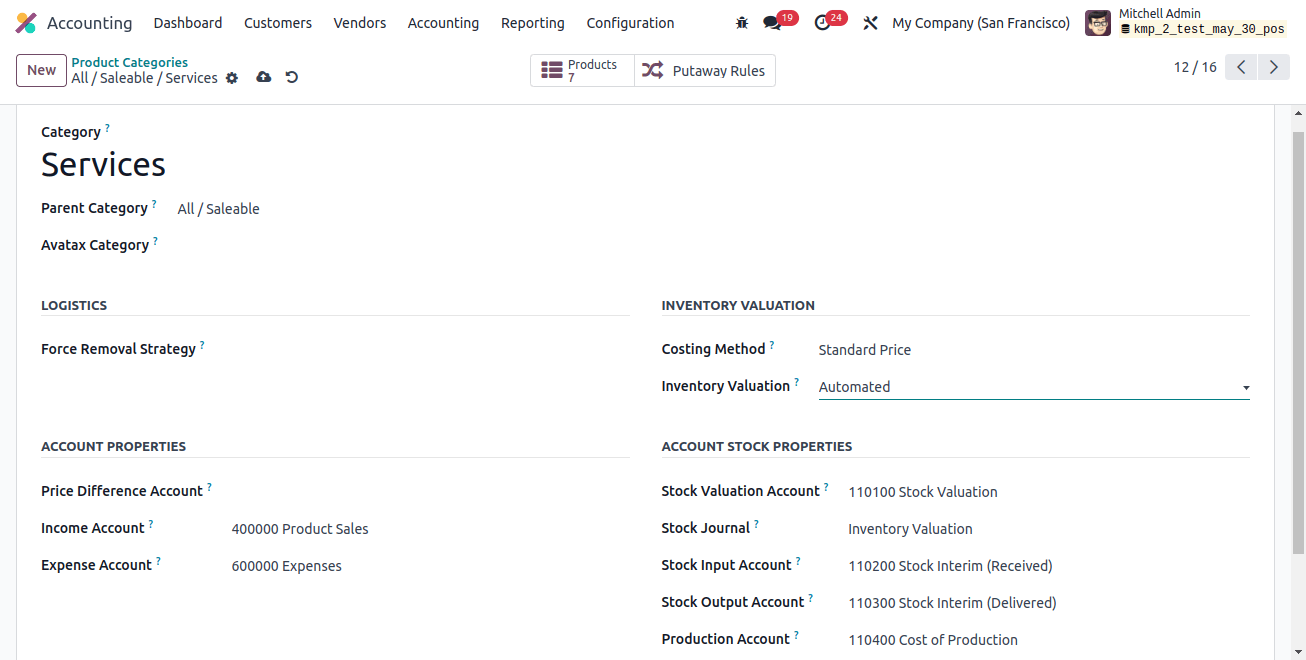
Furthermore, the costing method should employ either First in First Out (FIFO) or Average Cost (AVCO).
Now let's purchase an item from this category. The PO's formation has no bearing on the accounting. As soon as items are received, however, stock entries will be created.
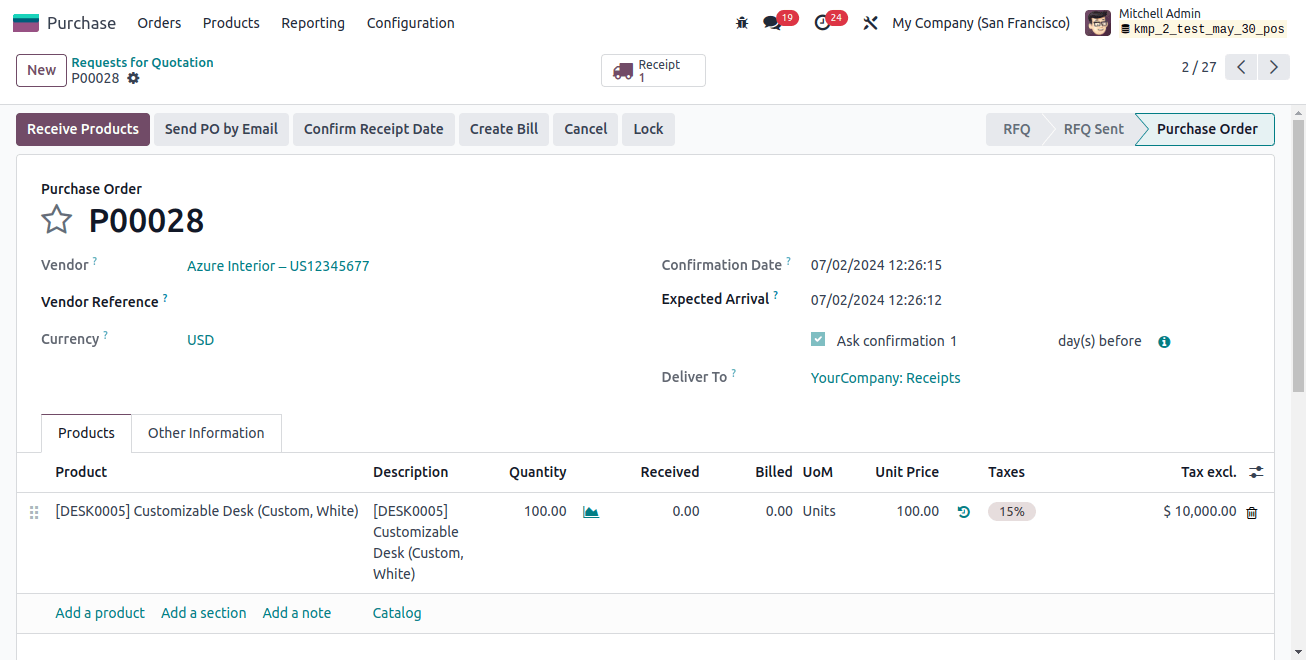
Making a purchase order (PO) is a way to document the business deal of the vendor "buy." When the stock is delivered, its value is recorded in the "stock input account," which increases the already existing stock value.
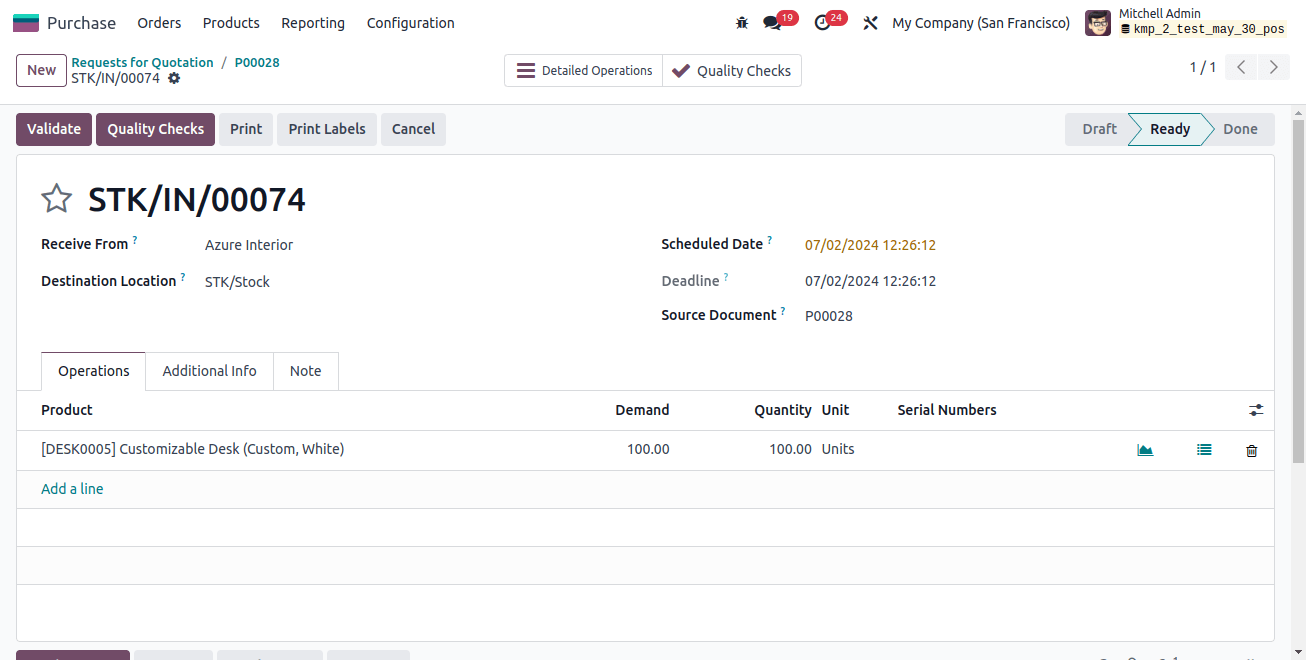
First, let's check the stock journal.
The stocks are viewed as a liability. When the asset value fluctuates, the asset-liability chart will dictate how the account is credited or debited. As a result, the stock valuation account is debited and the stock interim received account is credited. An account used for stock valuation holds the current asset value. Thus, the stock valuation account is debited if an asset appreciates.
The asset-liability chart defines which accounts are debited and which are credited when the accounts for assets and liabilities and income and expenses respectively increase.
The creation of the purchase order bill is the next task that will have an impact on the accounting ledgers.
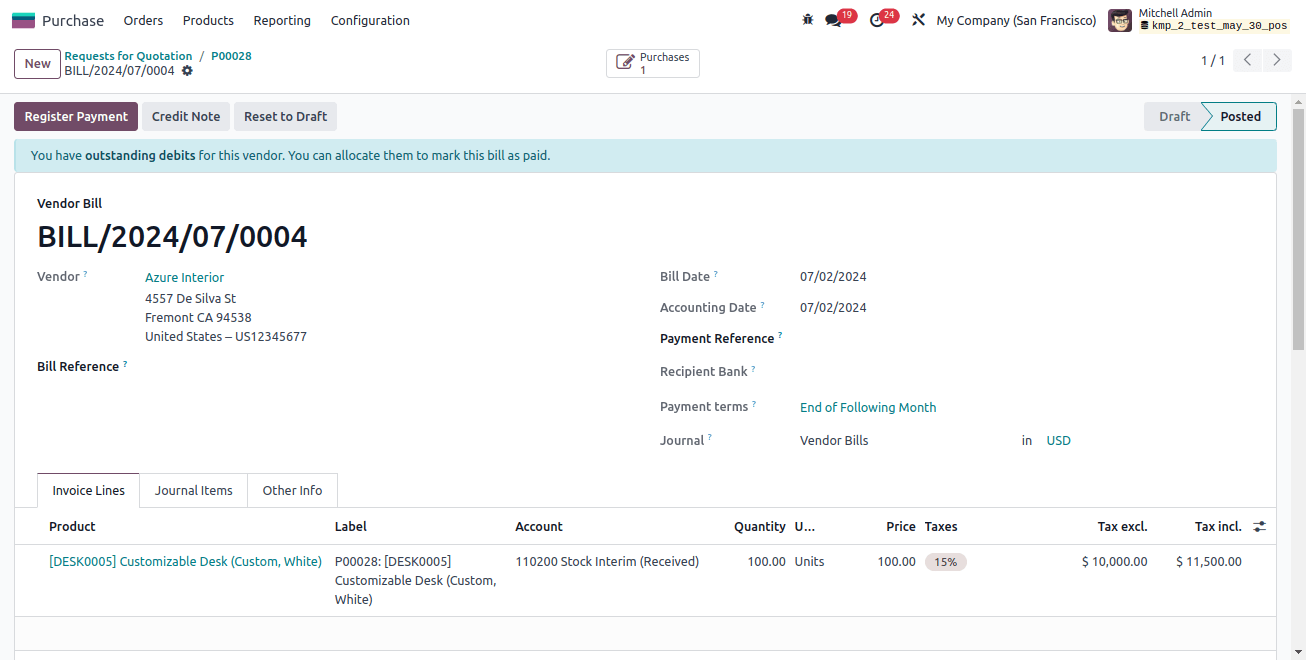
The following is the main difference in the Anglo-Saxon accounting systems. Instead of the expense in this instance, the account for interim stock receipts is debited. This is because, instead of having its expense documented in the ledger, the acquired item was recognized as an asset.
When asset value increases, the tax paid is also subtracted from the stock interim received account. The account payable, which is a liability that is credited when liability increases, has the amount that needs to be paid to the seller shown in it.
Once the payment has been recorded, the bill status will update to "In Payment".
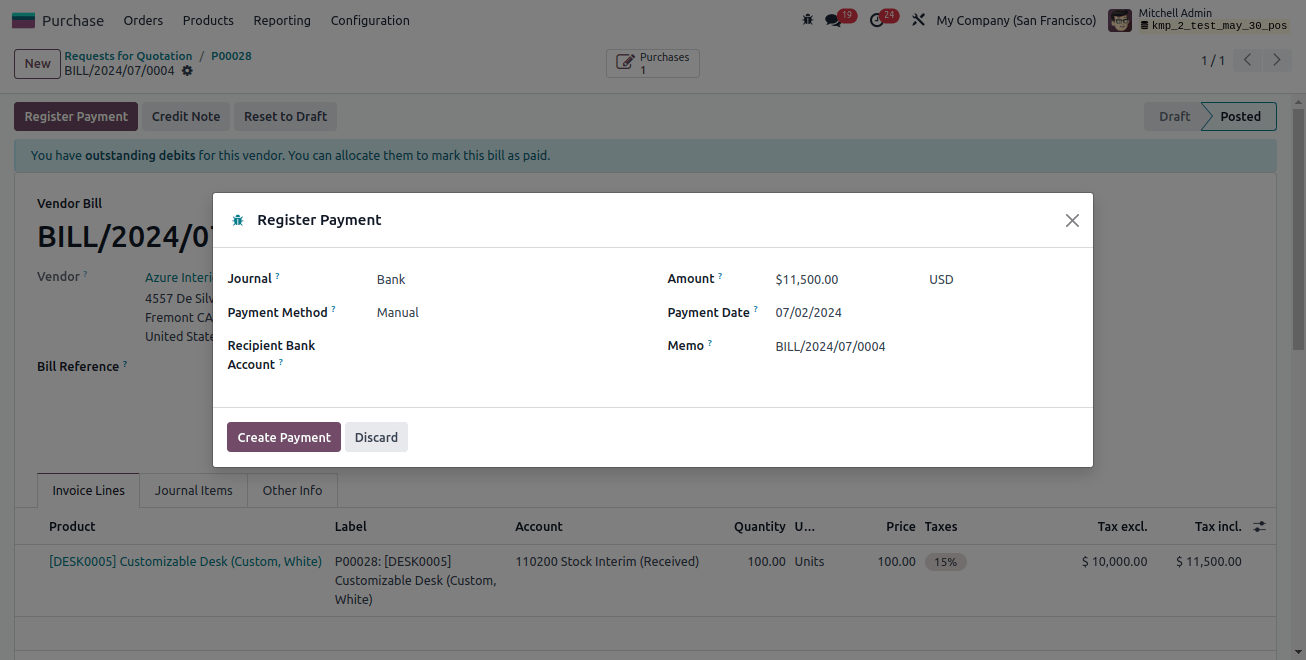
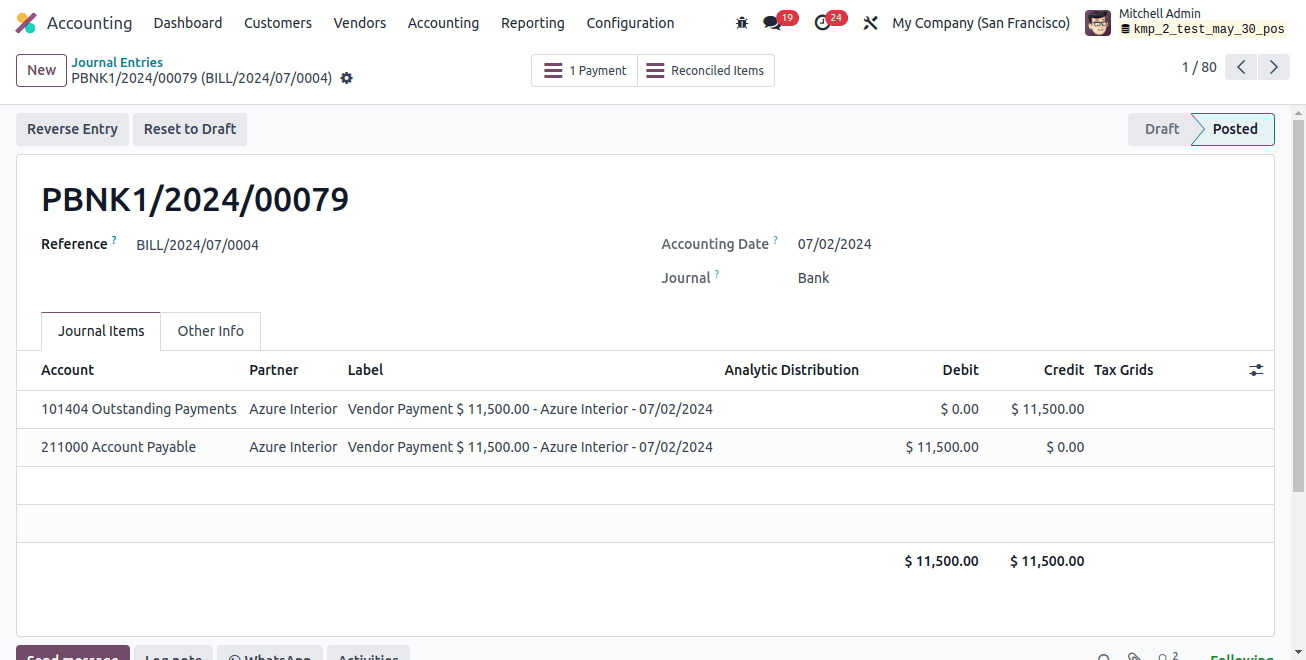
The outstanding payment account will then be credited in the payment journal entry, and the account payable will be debited (when liability falls).
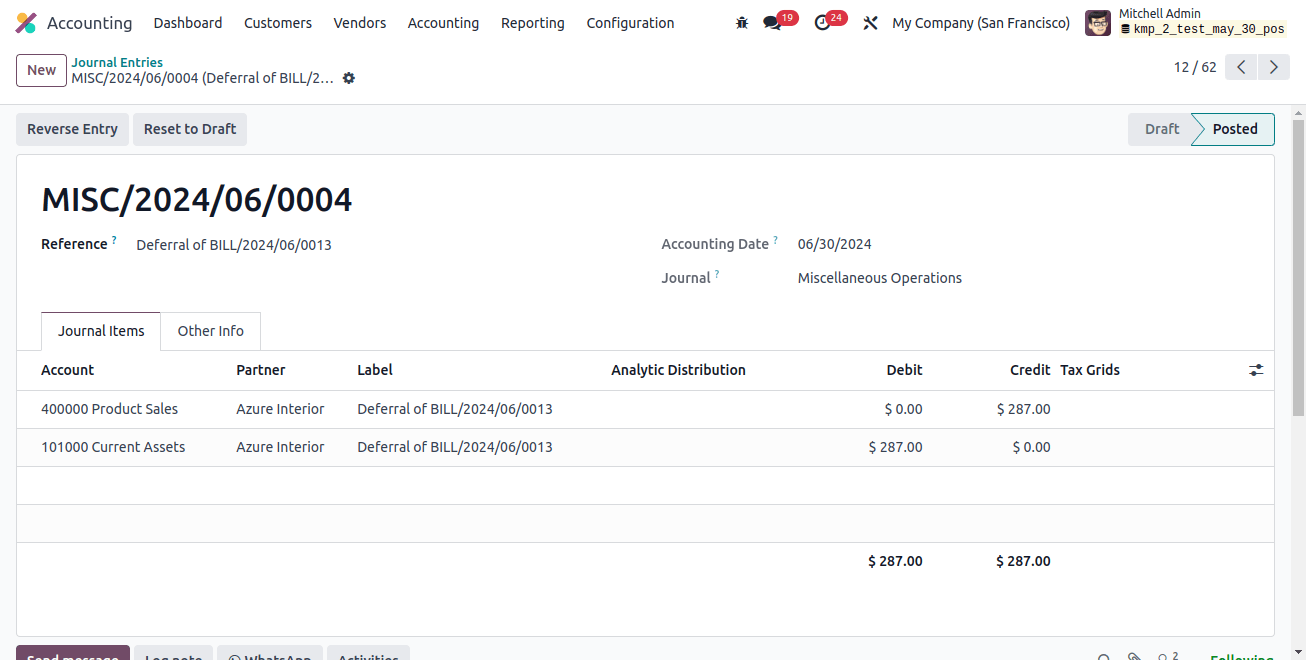
Reconciling the imported bank statement and journal entries for payments can be done later. The procedures for generating statements, importing ledgers, and balancing accounts in Odoo 17 are identical to Continental Accounting system.
Now let's go on to a sales operation where some of the products that were bought are sold. We initially paid a certain amount for certain volumes. It keeps it as a stock instead of recording the expense as a result. Right now, two quantities are being sold.
No accounts are touched when making a selling order, which is identical to producing a document.
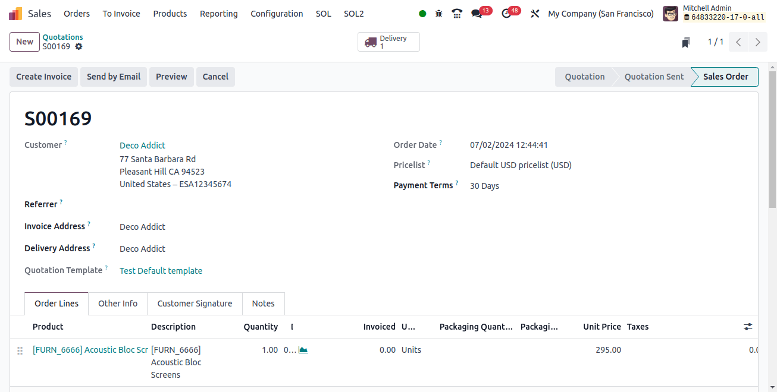
After the delivery is confirmed, stock accounts will be affected.
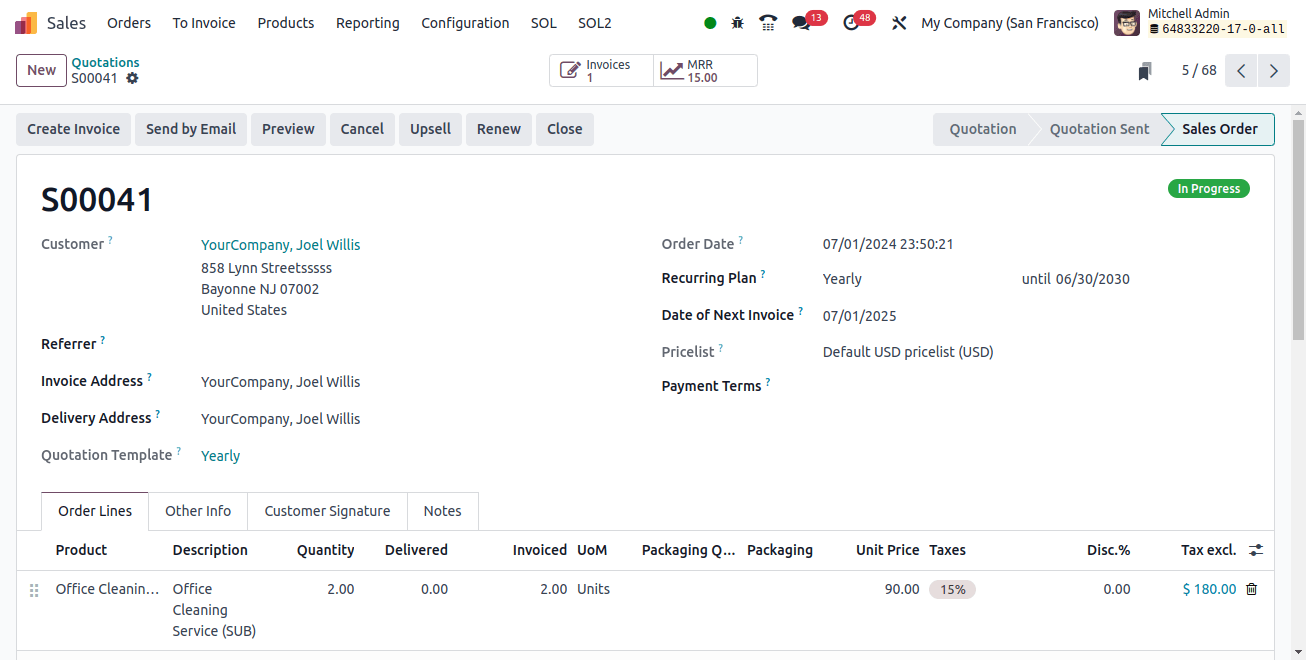
The stock journal, which displays the debit to the stock interim delivered account, is what we need to look at now. When the liability is sold out and the responsibility decreases during a selling activity, the account is debited. Since stocks are assets by definition, the account is used for stock valuation. Sold-out products cause the current stock value to decline, which reduces the asset and credits the account.
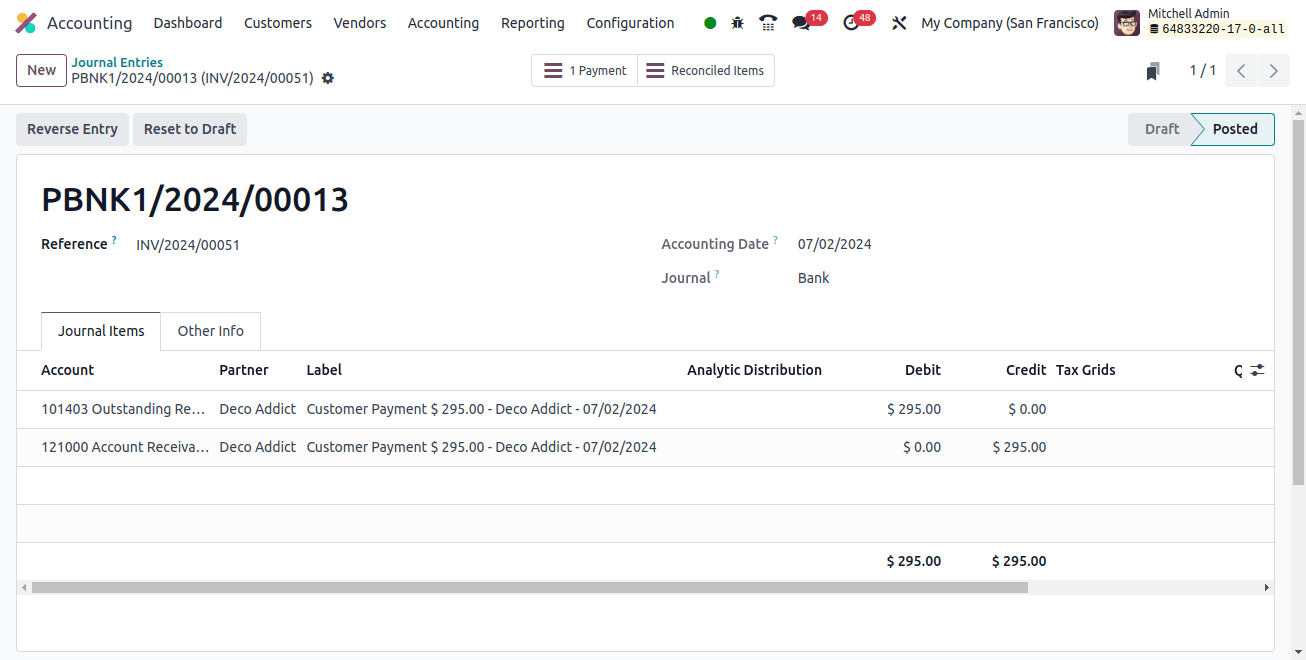
In this case, the sold products are only worth $295. The order invoice you now have will be posted and the cost will be recorded in the "Expenses" ledger.

This example's income account is "Product Sales," which is credited when revenue increases. The stock interim delivered account comes next. This time, the shortage of goods is noted and shown as an asset. As a result, the stock account that was briefly provided is credited and the expense is debited (increasing). We have now recorded the expense in the Anglo-Saxon accounting system.
The "tax received" is also credited since the liability increases. The asset known as the account receivable follows next, and it is deducted as it increases. Later on, this invoice can be paid and reconciled. The rest of the process and the ledger publication are similar to the continental accounting system.
This is how the Anglo-Saxon Accounting feature of the Odoo 17 accounting module operates. The product is listed as an asset; the expense is only affected when it is used up in production or other activities. Hence, Odoo Development unlocks efficient Anglo-Saxon accounting for streamlined ledgers in Odoo 17.
Related Post:


